LTE Arduino Hat Development Board
Basic Overview #
The LTE Arduino Hat Development Board is a fully integrated cellular communication shield that turns almost any standard Arduino board into a complete IoT device with real 4G LTE connectivity, 2G fallback, precise GPS/GLONASS positioning, voice call capability, and SMS functionality.
It is designed as a true “HAT”, meaning it is 100% pin-compatible with the Arduino Uno form factor and its derivatives. You simply align the headers and press it directly onto your Arduino — no soldering, no jumper wires, no level shifters required. This makes it compatible with a very wide range of official Arduino boards.
Supported Module List #
- Arduino uno R3
- Arduino uno R3 SMD
- Arduino Zero
- Arduino Yun Rev2
- Arduino UNO Wi-Fi Rev2
- Arduino UNO R4 Wi-Fi
- Arduino uno R4 Minima
- Arduino Leonardo
Feature List #
Module Features:
- Quad-band: 850/900/1800/1900MHz/LTE-FDD B1/LTE-FDD B3…
- AT Commands: Compliant with 3GPP TS 27.007, 3GPP TS 27.005 and Quectel enhanced AT commands3- TCP/UDP/HTTP/FTP/PPP
- Jamming Detection
- Audio
- FOTA
- Single SIM, Single Standby
- GPS+GLONASS
- QuecFast Fix
Development Board Resources #
Function Description #
The main component and interface placement of the Development board is shown in the following figure:

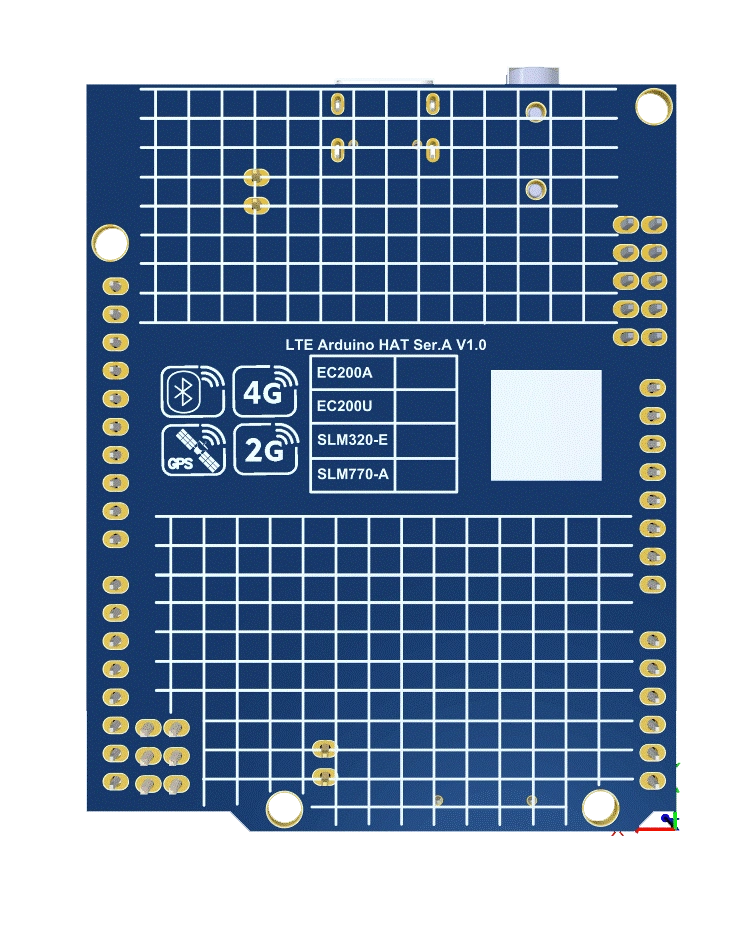
Development Board Configuration #
The detailed assignment of the peripheral interfaces on the Development board is as follows:
| NO. | Name | Silkscreen | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | USB Type-C Interface | – | – |
| 2 | Audio jack 3.5 mm | – | – |
| 3 | Sim card case | – | 4FF SIM Card 12.3 × 8 mm |
| 4 | Manual boot | BOOT | Push button |
| 5 | Manual Reset | RESET | Push button |
| 6 | Serial jumper | HRDW/SW | You can switch between hardware and software by changing the jumper position |
| 7 | External BT/WIFI Antenna | BT | UFL ANTENNA |
| 8 | External GNSS Antenna | GNSS | UFL ANTENNA |
| 9 | External GSM Antenna | MAIN | UFL ANTENNA |
The Development board has 3 functional indication LEDs, as follows:
- STA: LED Connect STATUS
- NET: LED Connect NET_STATUS
- D1: Power indication LED
The main pin placement of the development board is shown in the following figure:

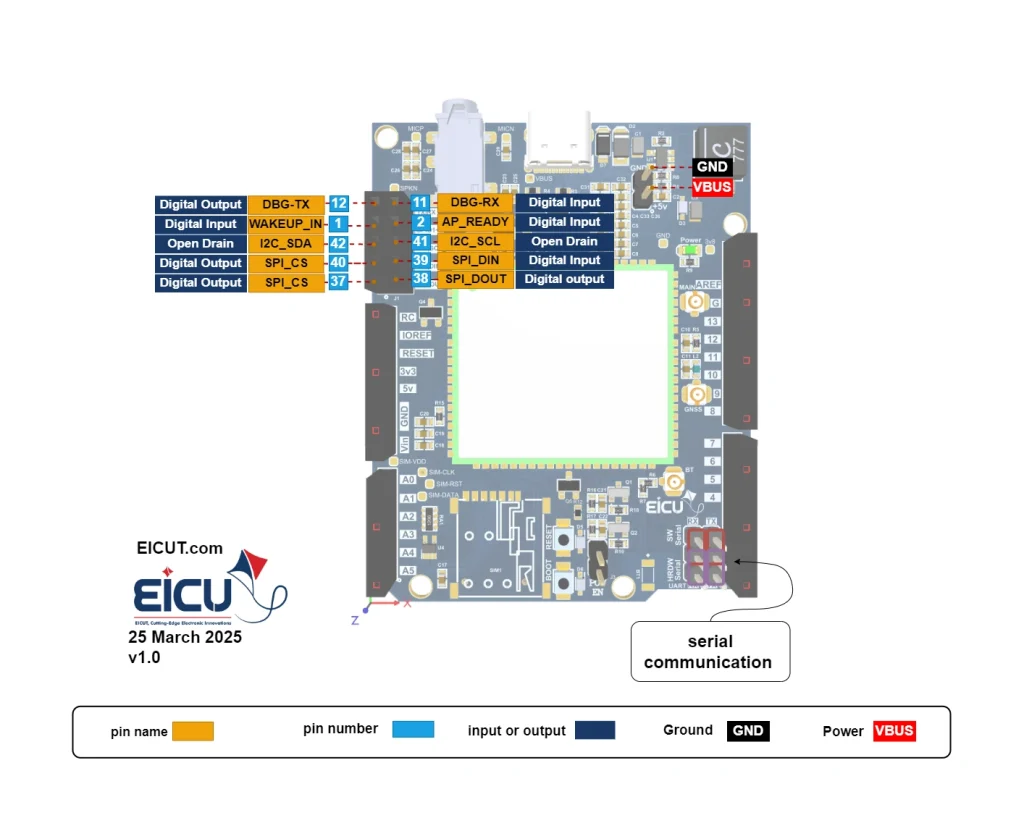
As shown in the image above, Arduino can communicate with the module in two ways:
software UART and hardware UART.
Development Board Interfaces #
- Power Header
| NO. | Name | Silkscreen | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8-Pin | NC | NC | – |
| 8-Pin | IOREF | IOREF | This provides a logic reference voltage for shields that use it. It is connected to the 5V bus |
| 8-Pin | RST | RST | Reset Arduino |
| 8-Pin | 3v3 | 3v3 | 3.3 V Arduino regulator – don’t connect to power the module |
| 8-Pin | 5v | 5v | 5 V Arduino regulator – Do not power the module from the Arduino, but the module can power the Arduino |
| 8-Pin | GND | GND | Ground |
| 8-Pin | GND | GND | Ground |
| 8-Pin | Vin | Vin | This pin is used to power the Arduino Uno board using an external power source. The voltage should be within the range mentioned above |
- ADC Header
| NO. | Name | Silkscreen |
|---|---|---|
| 6-Pin | ADC0 | A0 |
| 6-Pin | ADC1 | A1 |
| 6-Pin | ADC2 | A2 |
| 6-Pin | ADC3 | A3 |
| 6-Pin | ADC4 | A4 |
| 6-Pin | ADC5 | A5 |
The Arduino Uno has 6 analog pins, which utilize ADC (Analog to Digital converter).
These pins serve as analog inputs but can also function as digital inputs or digital outputs.
Analog to Digital Conversion
ADC stands for Analog to Digital Converter. ADC is an electronic circuit used to convert analog signals into digital signals. This digital representation of analog signals allows the processor (which is a digital device) to measure the analog signal and use it through its operation.
Arduino Pins A0-A5 are capable of reading analog voltages. On Arduino the ADC has 10-bit resolution, meaning it can represent analog voltage by 1,024 digital levels. The ADC converts voltage into bits which the microprocessor can understand.
One common example of an ADC is Voice over IP (VoIP). Every smartphone has a microphone that converts sound waves (voice) into analog voltage. This goes through the device’s ADC, gets converted into digital data, which is transmitted to the receiving side over the internet.
- Digital Header
| NO. | Name | Silkscreen | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18-Pin | PD0/TX | 0 | Serial Communication |
| 18-Pin | PD1/RX | 1 | |
| 18-Pin | PD2 | 2 | – |
| 18-Pin | PD3/PWM | 3 | – |
| 18-Pin | PD4 | 4 | – |
| 18-Pin | PD5/PWM | 5 | – |
| 18-Pin | PD6/PWM | 6 | – |
| 18-Pin | PD7 | 7 | – |
| 18-Pin | PB0 | 8 | – |
| 18-Pin | PB1/PWM | 9 | – |
| 18-Pin | PB2/PWM/SS | 10 | SPI Communication |
| 18-Pin | PB3/PWM/MOSI | 11 | |
| 18-Pin | PB4/MISO | 12 | |
| 18-Pin | PB5/SCK | 13 | |
| 18-Pin | Ground | GND | – |
| 18-Pin | AREF | AREF | – |
| 18-Pin | PC4/SDA | SDA | I2C Communication |
| 18-Pin | PC5/SCL | SCL |
- Header 2*5
| NO. | Name | Silkscreen | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2*5-Pin | DBG-TX | TX | Digital output |
| 2*5-Pin | DBG-RX | RX | Digital input |
| 2*5-Pin | WAKEUP_IN | GPIO1 | Digital input |
| 2*5-Pin | AP_READY | GPIO2 | Digital input |
| 2*5-Pin | I2C_SDA | SDA | Open Drain |
| 2*5-Pin | I2C_SCL | SCL | Open Drain |
| 2*5-Pin | SPI_CLK | CLK | Digital output |
| 2*5-Pin | SPI_DIN | DIN | Digital input |
| 2*5-Pin | SPI_CS | CS | Digital output |
| 2*5-Pin | SPI_DOUT | DOUT | Digital output |
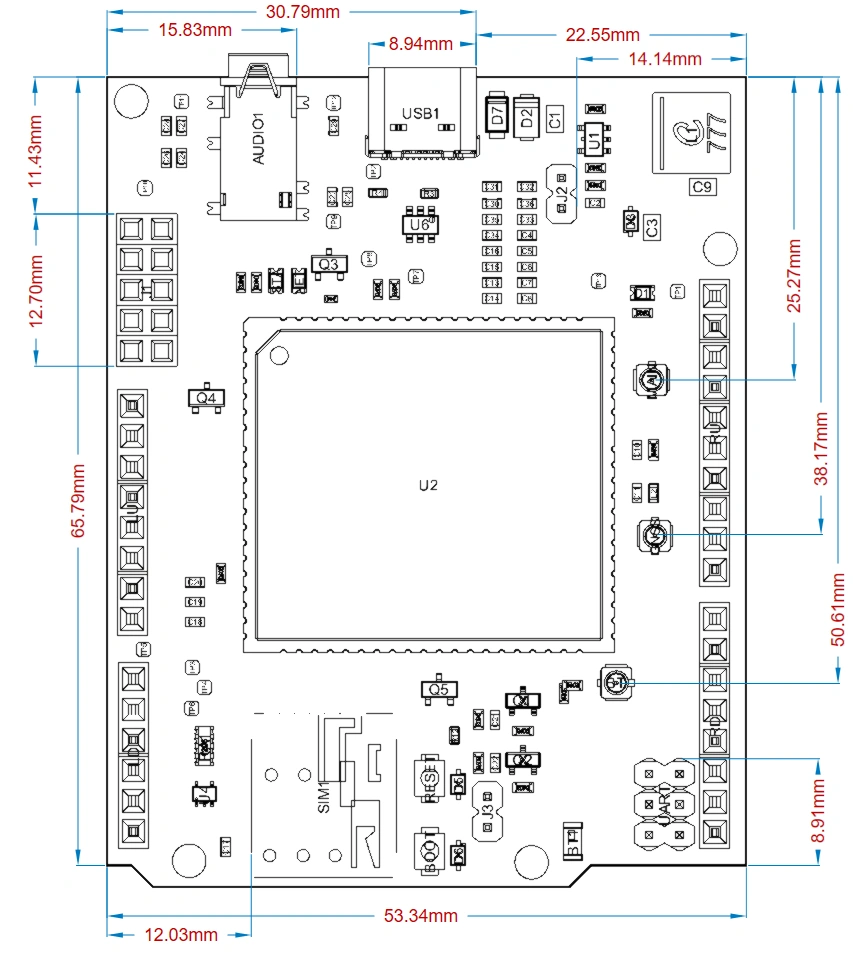
Development Board Dimensions #
Getting Started Preparation #
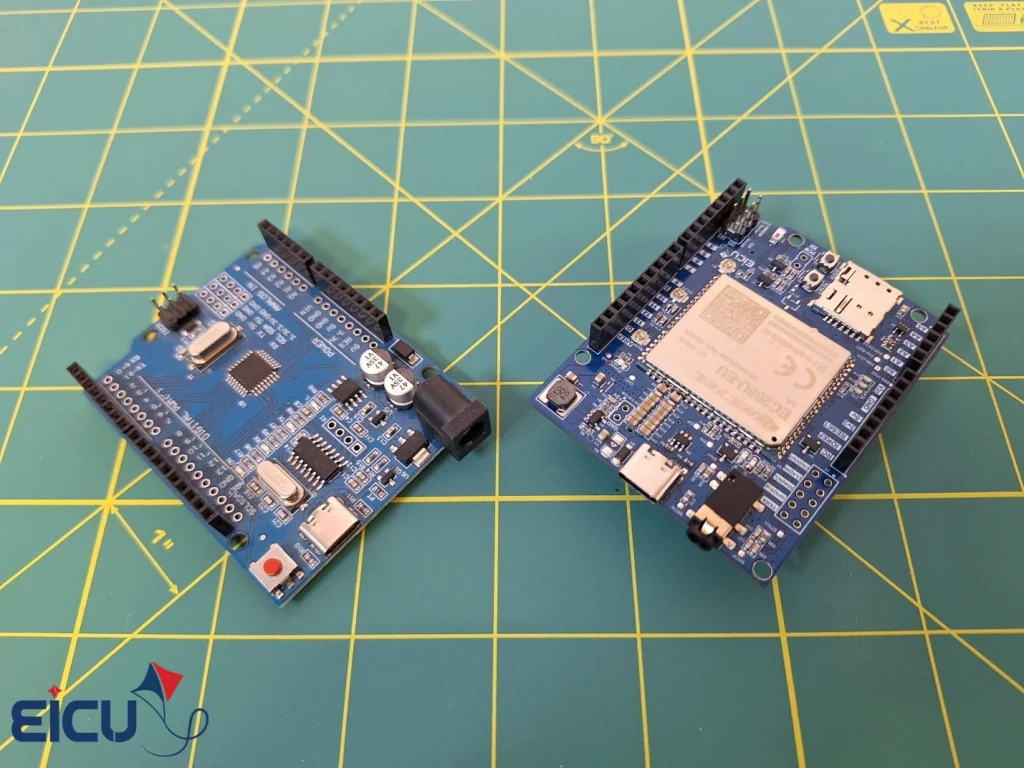
Suppose you want to make a call, send an SMS, or even get the location of a device in your project. There are many solutions available, and the Quectel modules are one of the good choices as a powerful platform for wireless communications. In this tutorial, we will show you how to connect the EC200 hat to an Arduino using the TinyGSM library and use it to send SMS messages and make voice calls.
Okay, before we dive into the coding part, let’s get the required components and libraries ready:
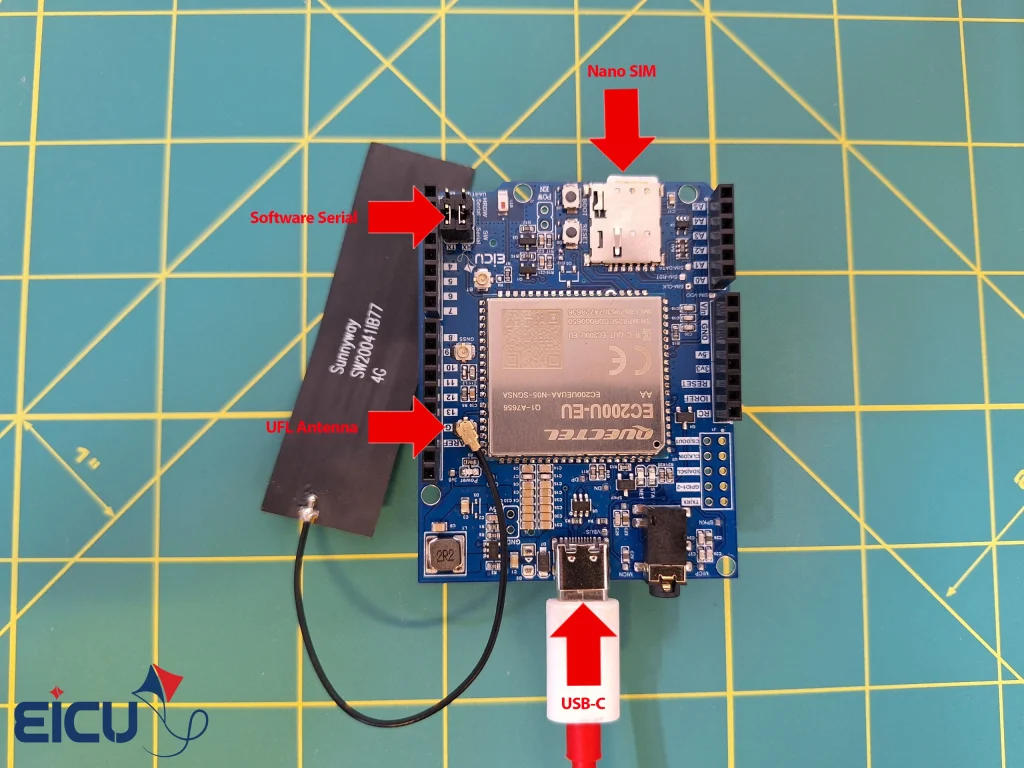
- EC200 hat: This hat is fully compatible with Arduino and is pin-to-pin. No additional wiring is needed.
- Software Serial Library: This library is used for the software serial communication between the Arduino and the EC200 hat.
- Jumpers: You will need jumpers to place the EC200 hat on the Arduino and to set the UART mode to software mode.
Preparation steps:
- Place the EC200 hat on the Arduino.
- Set the UART switch to the software mode.
- Configure the jumpers to the software mode.
Now that everything is ready, we can start coding and use the EC200 hat to send SMS messages and make voice calls.
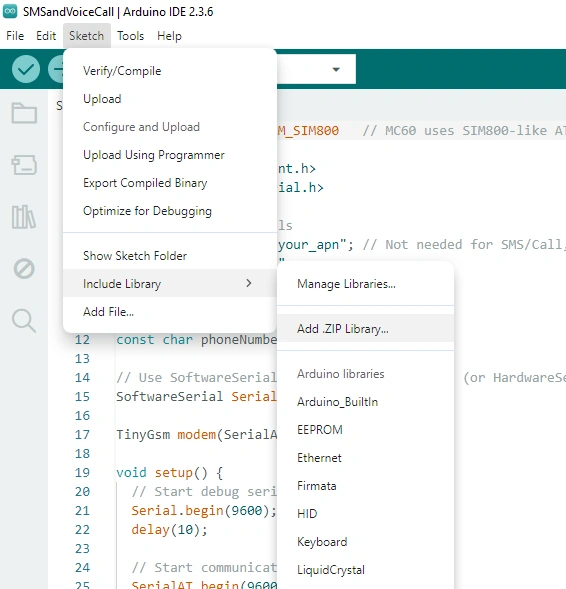
In next step downloading the library, we need to add it to the compiler.
(Like the image below).
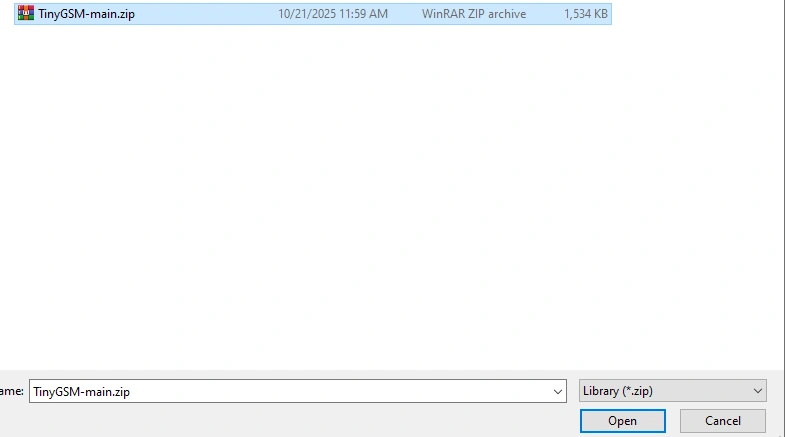
Once the library has been added, go to File -> Examples > TinyGSM > smsandvoicecall to select that example.
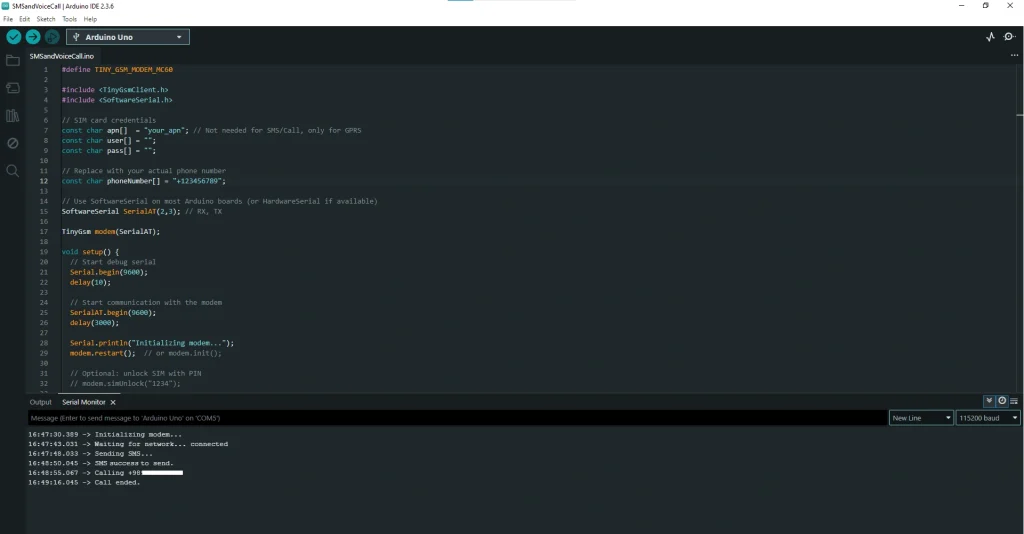
After opening the example, we need to make a few changes to the code:
- In the first line, replace it with the following code:
|
1 |
#define TINY_GSM_MODEM_EC200 |
- In line 12, enter the number that you want the module to call.
- In line 15, change:
|
1 |
SoftwareSerial SerialAT(2, 3); // RX, TX |
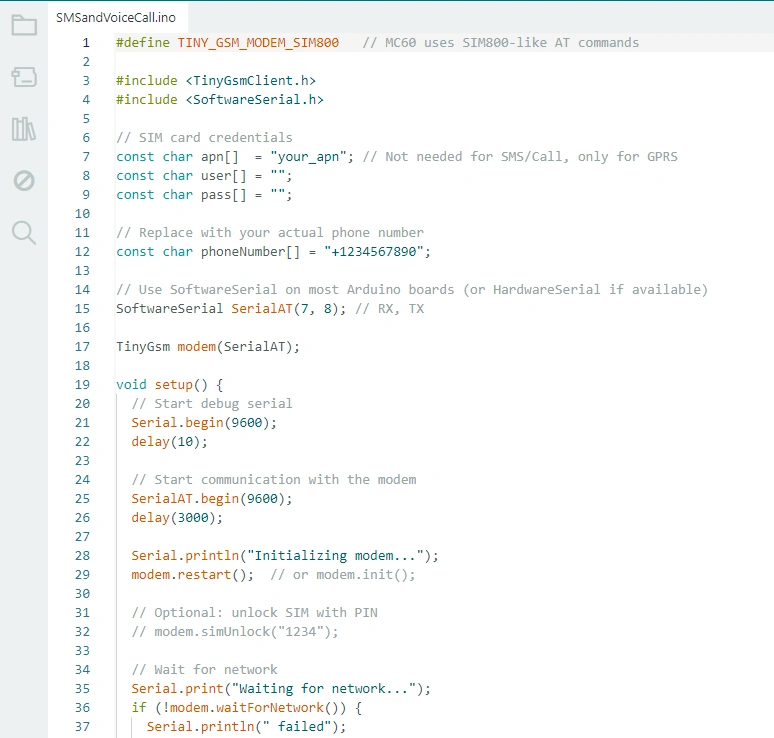
Important Note: If you encounter the following error while compiling other examples of this library or even this library itself:
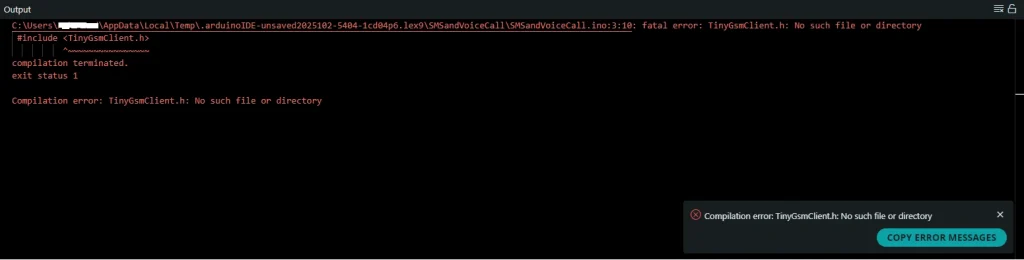
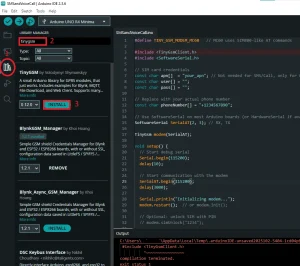
You need to search for and download the required libraries from this section. After downloading, a message indicating successful download and installation will be displayed in the output.
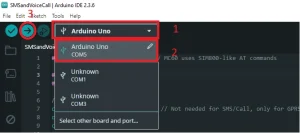
If you have followed the above steps correctly, the code will compile and be ready to upload to the Arduino. According to the image below, enter the model and COM port to which the Arduino is connected, and click on the option marked with 3 in the image to start uploading the code.
Upon completion of the compilation, place a nano SIM card into the EC200 hat (the operator does not matter) and connect the antenna to the UFL connector on the board.
The power supply for the EC200 hat is 5V, which you can connect from the header pins or via the USB Type-C port.
A very important note is that your power supply must be able to provide a peak current of 1.5 amps for the EC200 hat; otherwise, the module will reset.
Following the completion of the above steps, open the Arduino Serial Monitor and set the baud rate to 115200. The Arduino and the EC200 hat will start communicating with each other via UART, and their messages will be visible on the Arduino’s serial port.

Tutorial Code #
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 |
// This line of code specifies that the EC200 modem is being used, which uses AT commands similar to the M66 #define TINY_GSM_MODEM_EC200 // These two lines of code include the necessary libraries for working with the EC200 modem and using SoftwareSerial #include <TinyGsmClient.h> #include <SoftwareSerial.h> // These three lines of code define the GPRS network access details. In this example, they are not needed as we are only sending SMS and making calls const char apn[] = "your_apn"; // Not needed for SMS/Call, only for GPRS const char user[] = ""; const char pass[] = ""; // This line of code defines the destination phone number const char phoneNumber[] = "+1234567890"; // This line of code defines the SoftwareSerial pins for communication with the modem SoftwareSerial SerialAT(2, 3); // RX, TX // This line of code creates an object of the TinyGsm class to work with the EC200 modem TinyGsm modem(SerialAT); void setup() { // This section of code initializes the modem. It first sets up the debug serial, then establishes communication with the modem. After that, it restarts the modem and waits for a network connection Serial.begin(115200); delay(10); SerialAT.begin(115200); delay(3000); Serial.println("Initializing modem..."); modem.restart(); // or modem.init(); // This line of code allows unlocking the SIM card with a PIN // modem.simUnlock("1234"); // This section of code waits for a network connection Serial.print("Waiting for network..."); if (!modem.waitForNetwork()) { Serial.println(" failed"); while (true); } Serial.println(" connected"); // This section of code sends an SMS with the message "Hello from EC200!" to the specified phone number Serial.println("Sending SMS..."); if (modem.sendSMS(phoneNumber, "Hello from EC200!")) { Serial.println("SMS sent successfully!"); } else { Serial.println("SMS failed to send."); } // This line of code creates a 5-second delay before making a phone call delay(5000); // This section of code makes a call to the same phone number and hangs up after 20 seconds Serial.print("Calling "); Serial.println(phoneNumber); modem.callNumber(phoneNumber); delay(20000); modem.callHangup(); Serial.println("Call ended."); } // This function has no code written in it, as all operations are performed in the `setup()` function void loop() { } |