Learn Microcontroller Programming Professionally Leave a comment
Importance of Programming for Electronics Engineers
Nowadays most of the electronic circuits use micro-controllers and processors that need good programming level. But you as an electronic engineer can’t learn it in the university. Maybe you say it’s computer engineers’ duties, but they aren’t familiar with hardware limitations; imagine if a computer engineer wants to write a program that can use only 512 bit of RAM. So the best solution is the electronic engineers that have a good programming skills and know how to code professionally.
Here we want to challenge your programming skills, Are you ready?
Challenge
Nowadays that using ARM micro-controllers spread out rapidly, cause a big change in hardware design process, i.e. a 32-bits processor that has enough RAM & FLASH memory and presents high speed beside low consumer power. You might did not use Z80 or 8086 with hardness and complexity that Assembly calculation with 32-bits number made it like a nightmare, or even number calculation with whether fixed or floating point; today, technology changes this nightmare into a sweet dream, But technology still doesn’t solve the programming challenge.
In this article we want you to write a program (for 32-bits ARM micro) that counts how many one a 32-bit variable has E.g.
|
1 2 3 4 |
0x80000001 = 1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 -> 2 Bit Set 0x00000001 = 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 -> 1 Bit Set 0xF0000F00 = 1111 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 0000 0000 -> 8 Bit Set 0xA0000500 = 1010 0000 0000 0000 0000 0101 0000 0000 -> 4 Bit Set |
Writing this program is simple but in different ways, that we want to discuss. A Routine Program that Everybody Writes:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
int CountingBitsSet(int data) { int sum=0; for(int i=0;i<sizeof(int)*8;i++) { if((data&(1<<i))!=0) sum++; } return sum; }Certainly this is the simplest program that anyone can write but it will be so slow, because it must run on a cortex-m processor with a frequency about MHz, in compare with a processor with GHz freq. that of course it doesn’t matter. |
First of all, lets explain the program function:
There is a loop for every variable’s bit and check if it is one or not and increase sum as one detected. so why this program has a poor performance? First and the most important reason is loop (it seems to be necessary), second the calculation such as compare, bit-shift, ADD and the logical operation AND that needs to be calculated in every loop. We recommend you to read article” It’s not micro-controller fault, it’s about programming” to know how to improve the program performance.
After A Little Bit of Thinking You Write:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
int CountingBitsSet(int data) { int sum=0; for(sum=0;data;data>>=1) { sum += data & 1; } return sum; } |
As you see we deleted shift and compare operation, in fact they are in the loop; now we have better performance but not the best. Do you have any idea?
A Program that A Hardware Engineer with Micro-controller’s Knowledge Write
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
#define GetBB_Adr(VarAddr) ( (__IO uint32_t *) (SRAM_BB_BASE | ( ((uint32_t)VarAddr - SRAM_BASE) << 5) )) int CountingBitsSet(int data) { int sum=0; volatile uint32_t *RamBB = GetBB_Adr(&data); for(int i=0;i<sizeof(int)*8;i++) { sum += RamBB[i]; } return sum; } |
Cortex-m micro-controller series has an option named Bit-Banding; it means micro. allowed to access the SRAM memory bit by bit – both read and write. But how is it possible? The following picture can help you.
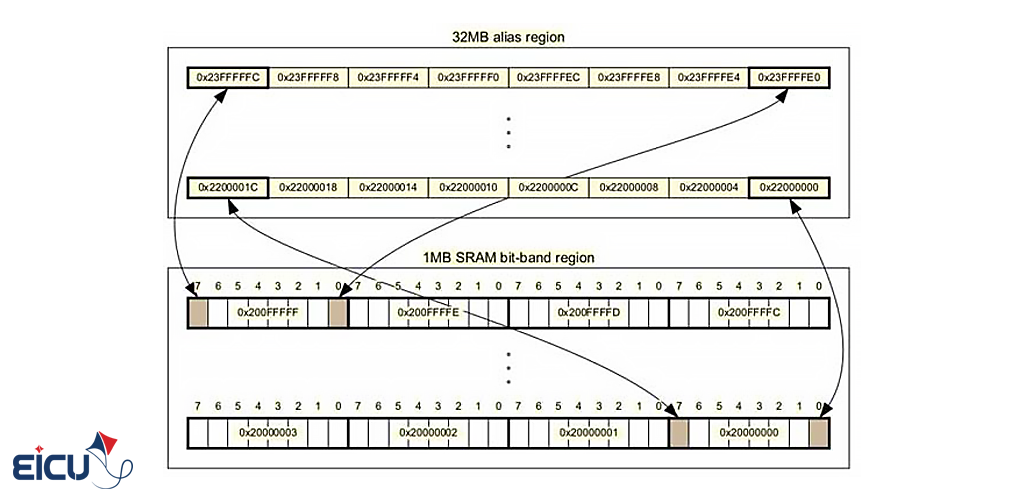
As you see, every bit of SRAM memory mapped with another address, that you can access every bit by reading or writing its address.
The Perfection One
We have been check some simple solution so far, using programming and hardware knowledge to perform the result, but can we perform it more? Of course, look at the following:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
int CountingBitsSet(int data) { static const unsigned char BitsSetTable256[256] = { #define B2(n) n, n+1, n+1, n+2 #define B4(n) B2(n), B2(n+1), B2(n+1), B2(n+2) #define B6(n) B4(n), B4(n+1), B4(n+1), B4(n+2) B6(0), B6(1), B6(1), B6(2) }; unsigned char * p = (unsigned char *) &data; int sum = BitsSetTable256[p[0]] + BitsSetTable256[p[1]] + BitsSetTable256[p[2]] + BitsSetTable256[p[3]]; return sum; } |
So we deleted the FOR loop and use the table that speed up the result a lot, in fact BitsSetTable256 table consists of a number’s bits from 0 to 255, means a bite:
This is a challenge for you how we made such a table with 4 line #define. Every 32 bits consist of 4 bites, if we calculate summation of every bite’s bits the result will be variable’s bits. This is the rest of code:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
static const unsigned char BitsSetTable256[256] = { 0,1,1,2,1,2,2,3,1,2,2,3,2,3,3,4, 1,2,2,3,2,3,3,4,2,3,3,4,3,4,4,5, 1,2,2,3,2,3,3,4,2,3,3,4,3,4,4,5, 2,3,3,4,3,4,4,5,3,4,4,5,4,5,5,6, 1,2,2,3,2,3,3,4,2,3,3,4,3,4,4,5, 2,3,3,4,3,4,4,5,3,4,4,5,4,5,5,6, 2,3,3,4,3,4,4,5,3,4,4,5,4,5,5,6, 3,4,4,5,4,5,5,6,4,5,5,6,5,6,6,7, 1,2,2,3,2,3,3,4,2,3,3,4,3,4,4,5, 2,3,3,4,3,4,4,5,3,4,4,5,4,5,5,6, 2,3,3,4,3,4,4,5,3,4,4,5,4,5,5,6, 3,4,4,5,4,5,5,6,4,5,5,6,5,6,6,7, 2,3,3,4,3,4,4,5,3,4,4,5,4,5,5,6, 3,4,4,5,4,5,5,6,4,5,5,6,5,6,6,7, 3,4,4,5,4,5,5,6,4,5,5,6,5,6,6,7, 4,5,5,6,5,6,6,7,5,6,6,7,6,7,7,8, } |
Final Challenge
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
int CountingBitsSet(int data) { data = data - ((data >> 1) & 0x55555555); data = (data & 0x33333333) + ((data >> 2) & 0x33333333); int sum = ((data + (data >> 4) & 0xF0F0F0F) * 0x1010101) >> 24; return sum; } |
So we can use this simple program! But how does it work? This isn’t a method that everyone can use; beside of writing such a program, understanding this program is not anyone’s job. Can anyone say how does it work?