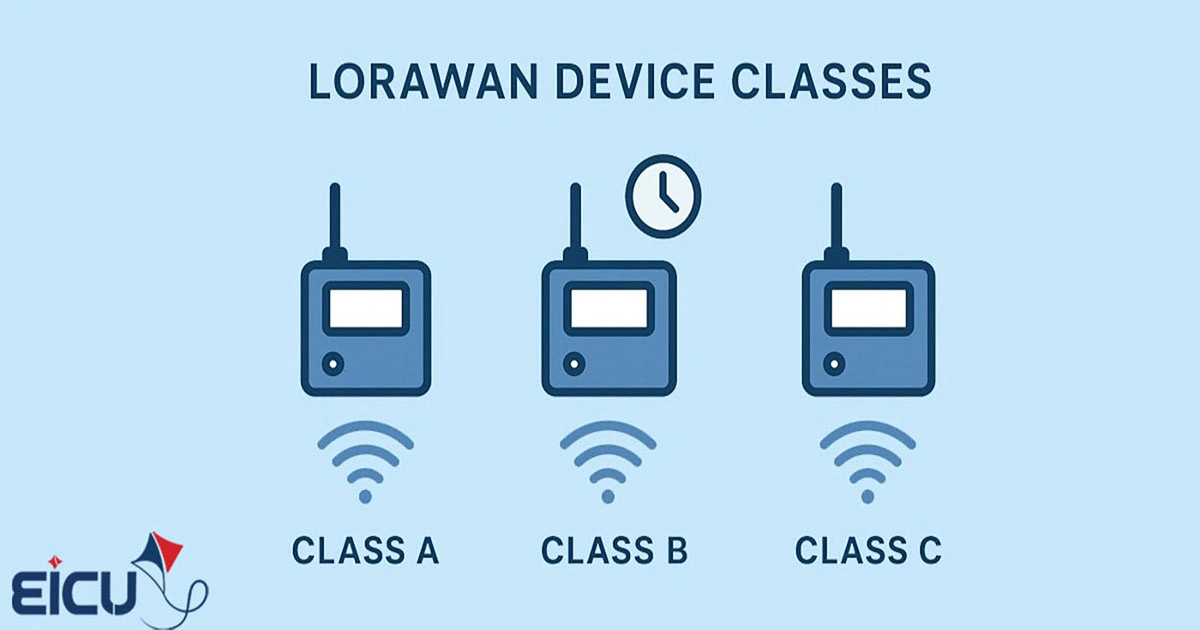
LoRa and LoRaWAN – Part 6: Introduction and Comparison of LoRaWAN Concentrators and Transceivers Across Generations
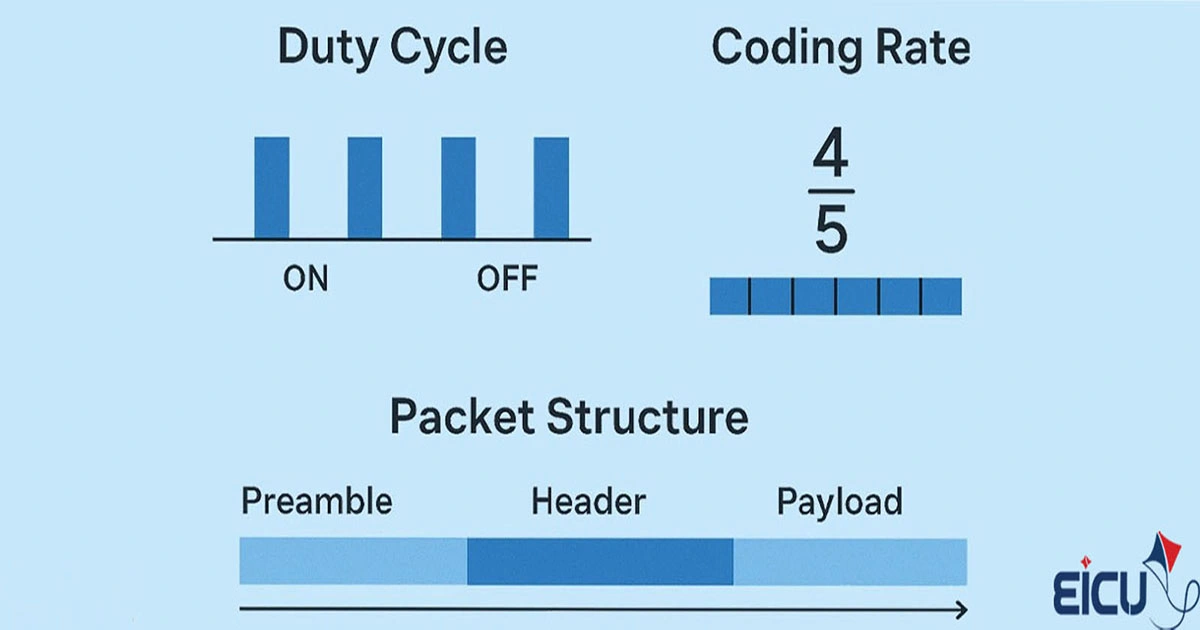
In the previous section, we examined Duty Cycle, coding rate, and packet structure in the LoRa protocol. Now that we are familiar with the nature and overall operation of the